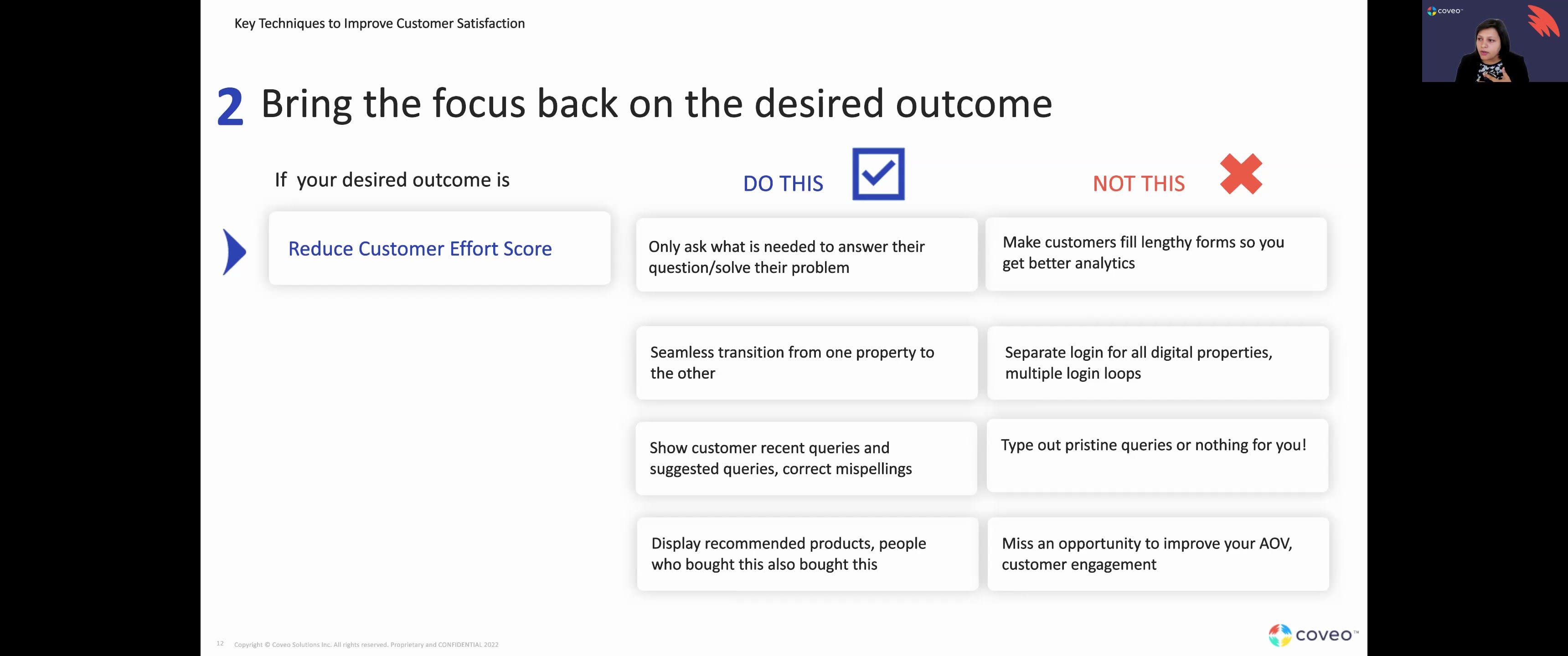
Good afternoon, folks. I hope everyone's doing well. Thank you everyone for joining. We will sit tight for a few more minutes just to allow everyone to keep, coming in, and then we'll, be on our way. Think we can get started, Thomas. Excellent. Thank you everyone for joining us today. It is quite a pleasure to be with you together this afternoon. We have an awesome webinar for everyone here on the line. My name is Thomas Kowiak. I work with our strategic clients at Coveo, working with them whatever use case they they they have and they leverage us for, to ensure that they see value in their partnership. I'm joined today by the awesome Lipika Rama, and, she is gonna be leading this presentation today. I'm gonna be taking on the role of moderator for today. So I will be sending in some polls. I do encourage everyone to participate and, send us your comments. We will record today's session. You will be able to receive a link for that recording afterwards. And, please do not hesitate at any time, in the presentation to either submit your questions in the chat or to raise your hand. We absolutely love, the, forum environment that we can create. So without further ado, I'm gonna turn over to Lipika for today's presentation. K. Thank you, Thomas. And welcome everybody. And, in today's webinar, we're going to talk about U. S. Best practices that drive customer satisfaction. This is part two of our, you know, U. S. Best practices webinar. So we did one earlier this month. If you haven't watched that, go back and watch the recording because we're gonna, you know, go over some of the concepts that we talked about in our first webinar as well. I'm Lipika Brahma. I'm a customer success architect at Coveo. I work in the customer success team. Thomas and I are on the same team. I provide additional technical guidance to customers to make sure that they reach their desired outcome quicker. So let's get started. So in today's webinar, the first things first, we'll do a very quick level set on what is CX, what is UX, what is UI because we'll be using these jargons repetitively and sometimes all over the place. So it's let's make sure we all know what all of this is about. We're gonna geek out a little bit on the stages of UX maturity. And, you know, we'll we'll try and understand where you are at at in terms of UX maturity within your organization. And that's the goal of this really. We look at some industry trends, and, you know, I've peppered in some industry trends throughout the presentation so we can look at, know, what is the industry saying and why should we be doing, what we're doing here right now. We look at some key UX techniques that drive customer satisfaction. Now when I say key UX techniques, we're gonna look at techniques that we have seen our customers employ and get to their business outcomes really, really quickly and really, really fast. So because if we start talking about US techniques, there's there's so many different things you can do. But we are trying to boil it down to if you have a Coveo implementation, these are things we have seen customers do and succeed. So let's focus on that today. And then we'll do a quick recap of everything that we have covered. So first comes first, let's get clear in all of our heads about the jargons. The UI is the user interface. So anything that you're interacting with. If it's a website, it is the search box. It is the facets. It is the filters that you can interact with on the website. So the visual elements of of what you're interacting with. The user experience is the interaction that you're having with it, whether you're going to find something, whether you're going to log a case, whether you're gonna purchase a product, all of that. The c x is the totality of UI and UX. So it's everything that comes from a visual interaction to what is happening in the back end. You have knowledge management processes in the back end that are supporting what you're doing in the front end. All of that is your CX. Now let's look at the stages of UX maturity. Right? I think it is important for you to understand what should be your next step, where you're at. So the this the the fact that you're on this webinar, you're wanting to know more about UX, you're not in stage one. You're you're good. You're not in stage one at all. It's not absent. So there are people in your organization that are thinking about UX, so you're not on stage one at all. Stage two is when you have, you know, limited focus on UX. So this can happen, you know, you're doing UX sometimes only for compliance reasons or for legal reasons. So for example, if you have a website that has to be accessible to make sure you reach different types of audiences and all of your customer base, that could be an example of it. So you're you're somewhat doing it, but you're not necessarily doing it all over your teams. There's no culture yet. If you are in this stage, what you need to do to get to the next stage is to focus on getting people to listen to what UX is, and how how it can help you. The next stage is the emergent stage. This can happen when you have smaller teams that are, that are, you know, focused on UI UX. You might have a leader that has done UX before and is very excited about it and is there to support you. But you still might not have it across all of your teams. So you might have it only in your support organization, but nobody's really thinking of it in your product. So that's where the emergent stage is. And if you are in that stage where it is there, but it's not consistently there across your organization, then you do for then you need to focus on building a culture around UX. Then comes structure. Now this is where most organizations are according to what, you know, the Nielsen group says. Most organization remain in the structure phase where they have different teams that are focused on UX. Every team has, you know, some capabilities where they are thinking about the desired outcome. They're thinking about UX. How do I make this better for my customer? There is some aspect of it throughout the organization. But there's still no cohesive strategy yet. So if you wanna go from structured to integrated, focus on having a cohesive strategy, which means that have that North Star that everybody is looking at. Right? Then we come to the integrated stage. And this means that everything is amazing. You have amazing leadership support. You have a North Star to look at. You have organizational direction. You have different teams that have budgets to do UX. It's a good place to be at. The only thing that can go wrong in this place is that you can become too focused on the process rather than on the outcome metrics. And the last thing, the last stage is user driven, which is you wake up thinking UX, you go to sleep thinking UX, and UX is your life. Right? So this is very hard to achieve. This is in organizations that are investing a lot in actual research projects that are sometimes even giving back to the community and giving back to the UX standards. Right? So this is hard to achieve, but not saying nobody can achieve this. But if you go there, it can often happen that you might fall back a couple of places if you're not paying importance to, again, that not star, that desired outcome, and your cohesive strategy. So now that we've discussed all of these stages, let's see where you think your organizations are. So Thomas launched a very quick poll on where you think your where you think you are on your company's UX journey. I see things coming in. That is great. I'll give a couple more seconds. Okay. Cool. Cool. And still gathering responses. Looks like the vast majority of you have answered that you are in stage four of a more of a a structured cohesive strategy. Amazing. So submissions have stabilized. We can quickly share results. So, again, yeah, vast majority of you and a few of you, are in that, golden state of the user driven. Yeah. The Nirvana stage of UX. That's great. If if you do wanna manifest yourself, we would be curious to hear from you and, debrief and and, get some takeaways from you. So, again, thank you all. Lipica, back to you. Thank you. Okay. So moving on. So we spoke about some talking about some industry trends. And the the reason I'm talking about this is we're looking at this at a at a perspective of, you know, what's happening in the industry? What should I be doing? What what are all my competitors doing? You know, what are other organizations doing that are of the same size that I am that are selling the same products that I am. Right? So the number one priority for organizations in twenty twenty two was, and I'm gonna say was because we're almost closing to the end, was, you know, growing business. And I don't think that's gonna change in twenty twenty three either. But the biggest challenge that was there in growing business was to improve content and knowledge delivery. That was the challenge main challenge that came when they wanted to grow their business. Because growing business doesn't just mean deflecting cases. It means, a lot of your users are coming to your site to understand more of your more about your product before they buy their product. People are doing their research. They're already qualified leads that are coming to you. They're downloading your white papers. They're downloading your videos. They're looking at your videos and then coming to you. Right? The second greatest priority for organizations in twenty twenty two was improving operational excellence. And I see this as going into twenty twenty three. You know, given the market situation we are in, I think operational excellence will probably become number one in twenty twenty three. And one of the top challenges that came with that was creating a seamless customer journey. Right? And we look at some strategies on how to do that. Now what did companies do to shift and understand, like, what did they do to tackle this? Right? So a lot of the organizations increase their spending on technology by a lot. So if you look at the spending that they're doing, they see a substantial growth in spending in technology. They are not spending as much as in facilities or travel and expenses because we're traveling less. They're not going to physical offices as much, but we're training our employees, and we're also hiring more experts into our company. So that's that's where we see the, you know, the focus happening. We'll do another quick poll to understand if that's what you saw with your organization as well. So, Thomas, back to you. The poll is launched. Again, we want to, understand, at least from this group, if you are aligned with this and, with this general trend that we do see. Looks like we are pretty even with about twenty answers. We're almost split fifty fifty, so that's always interesting to see. So we'll leave it open for a few more minutes, maybe a minute, and then we'll we'll get going. Mhmm. Okay. We have exactly twenty responses. Perfect. We're right fifty fifty. So, again, thank you all for for your answers. K. Thank you. Okay. Now let's focus on some key UX techniques to deliver improved customer satisfaction. Okay. So the first and foremost technique is map your customer journey. So this is the first thing that you have to do if you wanna deliver an amazing UX for your customers. You have to map their journey. You have to understand what they are going through to get to your product, to get to your service, to buy your product, to buy your service. You know, in some organizations, the buying process can be really long. But even then, you have to understand what they're going through in each process. How does your sales process look like? How does your, you know, lead process look like? All of that. So to do that, you have to map your customer journey. Sometimes you just have to go on your own website and look at what you see over there and what the challenges are for your customer. And when you're doing that, the most important thing to consider is the actor or the persona. And when I say actor, it's not a specific user, but it's a persona with the end goal. For example, on our website, we have customers coming in. We have partners coming in. We have our employees going there to search for things. It's different personas, but each one of them has a different end goal. Right? So when you're mapping your journey, make sure you take that into account, the different personas and what their experience should look like. What are they what are they experiencing while they're going through that journey? You look at the different scenarios, their expectations. You look at the different phases of the journey. You look at their actions, mindsets, and emotions. So for example, they are coming on your side and they're asking you, hey. Can I see a demo of your product? And there is a long form that has fifteen different fill fields that I have to fill. My emotions at that time will be like, yeah. I really wanna buy your product, but I don't wanna fill this really long form. Right? So those are the emotional aspects of things that you need to consider. Then you need to consider opportunity, and that's a very important part of it. A customer coming to your site, is your customer wanting to engage with you or your partner wanting to engage with you? So that's a very important time for you to grab their time a second of their time to to engage with them, to to to understand what they're trying to do. Right? So those are the opportunities that you should be looking at. So when you map your customer journey, it looks something like this, which is a template. And then once you've mapped it, it looks something like this where you're saying this is my persona. Their expectation is that I look at clear online information, and this is an example where a customer is trying to switch a mobile plan. Right? You look at so many different things that they're engaging with. They're not just interacting with your website. They're looking at different ads that are showing up in their Instagram posts. They're looking at marketing campaigns that are showing in their Facebook ads. They're watching TV commercials. They're also maybe bleeding flyers that you're sending to them. Right? There are different ways they're getting to that information. They're comparing, contrasting with different, you know, other providers. They're calling your contact center to say, hey. How do I get your plan? How do I fix this? Will you give me a discount because, you know, you're getting a new customer? All of those things. Right? All of those interactions are part of your customer journey, and each of them has an opportunity or a dead end that you might need to fix. So the first step is to map your customer journey. How does Coveo support this? Now a lot of our customers, they have different, you know, digital properties or physical properties. For example, a shoe store, there is a physical store that I can go to to buy your shoe, but I can also buy them online. So Coveo has access to anything that happens on your digital data, but doesn't have access to what happens on your physical locations. Right? Or data that you might be getting from your devices that you have in your customers' environment, in your customers' houses. So Coveo has all of the data in Snowflake right now. So we provide you with reader accounts and an ability to do data share, which means you can take this data and put it into any VI tool and map that entire customer journey by yourself. Anything that you have in Coveo, you can do somewhat of a mapping. But, if you want to do an entire mapping where you see from the start to the end of the journey, the best thing is to take out all the data, put data from different sources into a BI tool, and look at how the journey looks like. The second thing is bring the focus back on the desired outcome. What are you trying to do? Right? If your desired outcome is to reduce your customer effort score And reducing customer effort score could mean that, you know, you're making them think less or you're making them click less. So it could either be, like, something they do manually physically or it could be something you're reducing their cognitive load by giving them things by by default. So do this. Only ask what is needed to answer their question or solve their question. Don't make them fill lengthy forms so you can get better analytics. Right? They're coming to your site. You already know who they are. They're logged in. You know what per products they've purchased. You know a lot about them already. Why do you need to why do you need them to fill that out again? And Kuvio can help you with this. We have, you know, a case assist functionality that helps predict different different categories when you're logging a case. So it can help you with that as well. Seamless transition from one property to the other. No different logins. No multiple login loops between different digital properties. Show recent queries. Suggested queries. Correct if they're doing a misspelling or up spelling error corrected for them. Don't do this where you say, if your query is not alright, you're gonna see a blank page and nothing more than that. Right? And if you were in our first webinar, you remember a blank page is an opportunity. A no results page is an opportunity for you to go and say, hey. You saw a blank page. Maybe try these things out, and that might help you. Display recommended products. People who bought this also bought this. People who read this also read this. You do that because you wanna reduce the effort on your customer to go back and do the search all over again. Reduce that for them. Give them things to see already. And don't miss an opportunity to improve your average order value or how you engage with your customer. Because if, and if you were there in our first webinar, we talked about social proof, which means that other people are doing this. So it might be interesting. Let me check it out. That's exactly what people who bought this also bought this is. Right? If you see a long queue in front of a restaurant, it might be good. That's why people are going for it. And that's your social proof. But how do you do that in a digital environment? You do that by saying, hey. Other people also looked at this. Other people also bought this. Or these are queries that other people did. So you reduce the effort that they have to take to go through the journey with you. So we're gonna talk about self-service a little bit because we're gonna talk about a customer case study where this particular customer wanted to improve their self-service and wanted to reduce support costs. So if you look at some industry trends, this comes from TSIA, the technological, you know, they do a lot of studies on the the overall trends in the service industry. What they have seen is, you know, the preferred support channel of self-service has grown from seventy one percent in twenty twenty to seventy five percent in twenty twenty one and even more in twenty twenty two. Also, the kind of cases that are coming through are mostly, how do I do this? How do I do this with your product? How to questions, which means that twenty five percent of these cases could have been deflected. One out of four cases could have been deflected, which means all that is all savings for you. Right? Because they're not coming into your environment anymore. Gartner also predicts that by twenty twenty five, organizations that focus on CX or or the customer experience will convert sixty five percent of their interactions into self-service. Think about that. If your customer can self solve without having to log a case, that saves them time, money, effort, and does the same for you as well. Now let's come back to the case study. So this case study is of a customer who whose business outcome or the desired outcome that they wanted to have was to reduce support costs. How do you reduce support costs? Log less cases. Right? Log less cases get customers to do more on their own. So improve your self-service success or you deflect more cases. Now this is how what a service blueprint looks like, and don't go too much into the complicated diagram, but basically what it means is everything that is there to support your customer to their journey. Today, we're gonna look at the customer journey of what happened with this customer. We looked at three different customers. One customer that, you know, saved eighteen million a year on support cost. Customer b showed an improvement in MPS, and it sustained for a really long time. And customer c is the customer we are talking about who wanted to be everything that a and b were. Right? Let's look at the traffic, and this is why customer journey is so important. Let's look at the how how the traffic went. Right? So if you look at the traffic, hundred and forty five percent more traffic was on the community for customer a, which means a lot of their customers were going and self serving before they went along the case. Okay? If you look at customer b Yeah. A lot of their customers also were going to the community. Four hundred percent more traffic was on the community as compared to the case deflection page. We look at customer six, quite the opposite. Customer c, seventy seven more traffic was on the case deflection page. And when we spoke to them, we we got to understand more about their customer journey. And one of the things that was happening was customers, while they were in the product, if they had a question, they were given a link and that link would lead them directly to the case creation page. Now which is why it's very important to map your journey and think about what outcome you're going for. If you're going for reducing support costs, you shouldn't be sending them to create a case right away. Send them to the community. Let themselves serve a bit or give them the results right in the product. They don't even have to go to the community. Right? So this is kind of like an example that showcased how going back to what your business outcome is and also mapping the customer journey is so important. Now, I know a lot of you also, you know, have similar setups where you have a community and a case deflection page. So we wanna learn a little bit more about you as well. So Thomas is again gonna poll you one more time to see how you see the traffic coming into your community. The poll is live, folks. K. We have about fifteen answers with the vast majority of you, focusing on the community portal. Which is amazing. Okay. I think it has stopped, so we can stop the poll, I guess. The thing. Yeah. About eighty percent of you, did indicate that, you were focusing your efforts mainly on the community portal, which is aligned with what Lipika was covering today. So that's music to our ears. Yes. Definitely. Okay. The third thing is improve content findability, which means you want your customers to find your content quicker. So what do we do? Move your content to where your customer is. Your customer doesn't have to go to your content. Your content goes to your customer. Proactively suggest content or products. And I know there are some things that I'm repeating, but they all go with that same idea of reducing, you know, improving customer satisfaction. We connect all the relevant sources into a easy easily searchable interface. What does what does this mean? If your agents have to log in to Jira, have to log in to Confluence, have to log in to Salesforce to find solution for one problem, that is not reducing their effort in any way. Right? And same for your customers. If they have to log in to three different things and figure out what's going on, that's not effective for them. That's not gonna lead you to customer satisfaction. Let's bring it all together into one interface. Grab all the metadata that you can, and the more, the better. Less metadata is never good. The more metadata you have, the more you can grab the best you get the best results from that. Coveo looks at these metadata as when when we are doing these searches. We look at title. We look at keywords. We look at different fields that you have. So the more metadata you give, the better it is for us. How does Coveo support this? So when we move your content where your customer is, you see an in app experience or the IPX experience or the Coveo insight panel experience where we are showing the results right in the service console. We proactively suggest content and products, content recommendations, product recommendations, query suggestions. We move all of your sources into one index. You still have the same security, so you don't, show internal content to external audience, but you can have all of them under one roof, under one UI. The more metadata, the better. So we can help with that. The the reason we say more metadata, the better because you can use them for manual tuning. You can use them for machine learning for so many different things. Right? So a lot of times customers get, you know, adaunted by this thing where we say more metadata because it's not easy to go back to go back and tag all your content with metadata. Right? So we can help you with that with a little bit of preprocessing with indexing pipeline extensions. And we can grab things from different fields and make new fields for you so you don't have all of that burden on on on your head to simplify that for you. Now this is another trend and it goes back to everything that we're talking about is organizations must get to know their customers again. We cannot rely on pre pandemic data because the behavior patterns have changed so much since twenty twenty that we cannot say, you know, we knew that our customers wanted this two years ago. It's the same thing that they want. We we cannot rely on that. And the reason I say that is we wanna personalize. So why do you want to know what your customers need is you want to do personalization in a way that helps your customers. So personalize, but keep it simple. So you can personalize in a way that gives your customers the right information, and you can hide the information that is not for them. Right? It can be a little tricky to do this on a public website because you don't know a lot about your customers yet, but you can still, deploy different machine learning algorithms that can help you with this. Now how does Coveo support this? Coveo supports this by what we call as custom context. And it sounds very complicated, but what it means is metadata. That's exactly what it means. If we know more about your customers, we can send that information to our machine learning algorithms, and we will create these buckets of behavioral patterns, And we understand exactly what to serve to who. Right? And you obviously have, you know, reports and dashboards that are there in Kaver that will tell you what your customers are clicking on and what they're what they're looking for. But, you know, our ART model, our recommendation model, any of these models, the more information you give us about your users, the better these models behave because we have to understand the context of your business. The and this is the last one, but a very important one is we have to prototype. We have to test test and test some more and then launch. What does this mean? So when, when you have, you know, different UIs that you're launching or different experiences that you're launching, it can be very daunting because you don't know how your users will react to it. So having a prototype and then running it by a pilot group of users can be very, very helpful to give you, you know, that that feedback to you saying that, okay. This worked and this didn't work. This helped our customers. This didn't help our customers. Pilot studies are often helpful when when you're deploying something for your customers, and you have a few customer champions who are very vocal about what they would like to see in your product, what they what they don't like about your product, or what they like in your customer service experience and what they don't like. And these pilot studies can help you understand that, and you can you can kind of close the circle with the analytics that you're seeing and mix that data and figure out what you need to change on your system. You can even AB test. Now the AB test is a more, how to say it's a little bit of hands off approach, which means that, we don't see we are not talking to these users directly, but we are doing we're we're kind of splitting traffic and see here fifty percent of the traffic will see this UI, fifty percent will see this UI. And we kind of compare and contrast with analytics and see which one is yielding better results. Now how does Coveo support this? We have an AB testing mechanism inside the Coveo platform that you can use to, you know, test out your different hypothesis that you have. You also have analytics that will tell you this is what happened in the a pipeline. This is what happened in the b pipeline. You can compare and contrast and see which one works out for you better. So these are all the key techniques that we have seen customers employ and get really, really good results. Now, I'm gonna stop really quickly because the next step is the recap. I wanna stop really quickly to see if there are any questions, any comments, any suggestions. Gonna wait a couple of minutes to see if there are questions. Any questions on any of the features that we discussed like IPX, AB testing, any of the machine learning models, the recommendation model, the query suggest model? Feel free to raise your hand, folks, or, drop your questions in the q and a section should you wish. K. It looks like someone has raised their hand, Thomas. Yes. Where are we at? Yes, This is. So one question I have, is, we have the ML, ML, from Covio. Right? And is it paused you mentioned that more metadata will be able to, some of the specific content to users based on their preferences or based on their past behavior. Mhmm. Is it possible for us to identify, based on the past behavior to map a user to the product of, the person's interest based on whether based on whether the past past cases created or past facets they clicked on, basically, all the events that we collect. Is it possible to identify, you know, a user a user's interest, products so that we can serve the content specifically, from those products to that person when when the when they're on our customer customer portal? Yes. So I will say there there there are different techniques you can do this. The first one I will talk about is a more generic approach where we are saying, we are looking at the the user search patterns or the things that, like you said, what facets they're clicking, what are they searching for, what product are they clicking on. We kind of look at all of that behavior, And based on we call it the user action history and based on the user action history, the next time another user does similar behavior or similar searches, we will make sure to put those kind of products on the top. So that is a very generic approach. Right? But it still works because we are learning from massive amount of data. So we can build these, different behavioral patterns, and we can still help customers get to the product of their interest quicker. The other way to do this is, if you have you know, I know some customers do this. They have a logged in community portal, and they will know what their what products their customers have purchased or what products they have interest on. And if you have a field that tells us that, that's the best way to do it because it's already telling us what these kind of customers want. And the next time they come, we will suggest similar products. But, yeah, what we can do is the first approach is you can use multiple different types of ML models. You have the ART model already. We can also have what we call the DNE model, which is the dynamic navigation experience. What that model does is it learns from facet selections, and it'll look at, you know, which is a facet that was selected last time, what content was selected, or what product was selected after that. And the next time it happens, it won't even need the customer to select the facet. It will automatically boost that content to the top. So I hope that answered your your question, PC. Yeah. Sure. Okay. Thank you. Okay. There were some, questions, in the q and a section, folks. So, again, the recording of this presentation is going to be available. And if you want to hear more about how to set up AB tests, there are some documentations that were made available there as well. Yeah. And I'm just looking at the question. You definitely don't need any tech team for the a b test. The Covio a b test module is very plug and play. You can do all of that in the Covio platform. So you definitely don't need any developers for that. You just need your hypothesis and the Covio platform. That's it. Mhmm. Okay. So there are no more questions. Let's move on to the recap. So we discussed a lot of things today. Right? But if we if if we had to put it put it all in one slide and say these are the things, let's focus on this. Mapping your customer journey is very, very important. Please do not skip this part because this will give you valuable insight to what your customers are expecting from you. Right? Focus on the desired outcome. Always bring back the focus on what am I doing this for. Am I trying to reduce support costs? Am I trying to reduce customer effort? Then what decisions will I take that will go directly against that business outcome? Or what decisions should I not take that will hamper that business outcome? Improve content findability, and this is a really important topic. I know we've been hearing content is king, content is queen forever, but it still is because that's what your customers are looking for. Either if they're looking to buy your product, they still want to read through your content. If they're looking to use your product, they still are reading through your content. It's it's it's it's it's still the most important part of your UX, strategy. Personalization, also a very important part of your UX strategy because you want to reduce the effort on the customer. So you want to personalize things for them so they don't have to do the same things over and over again. Prototyping and testing, again, is a very important part. The last thing before you do before you launch because you're prototyping. And when I say prototyping, sometimes it might sound like, oh, that's for products, but I don't have a product. I have a service. It doesn't matter. You can still have your customers come into your experience, design it for them, make them use it, get their feedback, act on their feedback, and then launch the product. So with that, these are all the, you know, key techniques that you need to drive, you know, good UX and drive customer satisfaction. If there are any more questions, please feel free to, you know, post them now. We'll keep the lines open for some more time, but I hope you had a, you know, good, session today and you learned something. If you have questions later on, feel free to send them our way as well. And, happy Thanksgiving. We'll just keep it open for some more time if there are any questions. Thank you all. Again, quick reminders, you are going to get a recording of today's presentation. Let us know if you have any other resources you want to have access to. Okay. I see the attendees count going down, which means that people are getting to Turkey Day faster. So Godspeed, everybody. Thank you so much for joining today, and have a great Thanksgiving and have a great holiday. Thank you very much.